Many customers believe that the cost of a transformer is limited to the amount that they pay upfront. At a basic level, transformer costs are determined by the time and materials used during the manufacturing process. However, the truth is that transformer costs are impacted by numerous complex factors, particularly when considering the impact on the overall system in which they're installed.
Recent Posts
How to Select the Right Transformer Manufacturer
When sourcing a standard or custom transformer, it is essential to choose a quality manufacturer to ensure the product functions as intended. However, given the large number of potential options available, selecting the right one can be challenging. Here are some of the key factors to consider when vetting transformer manufacturers to help you choose one for your application. Request a Quote
What to Consider When Constructing Power Inductors
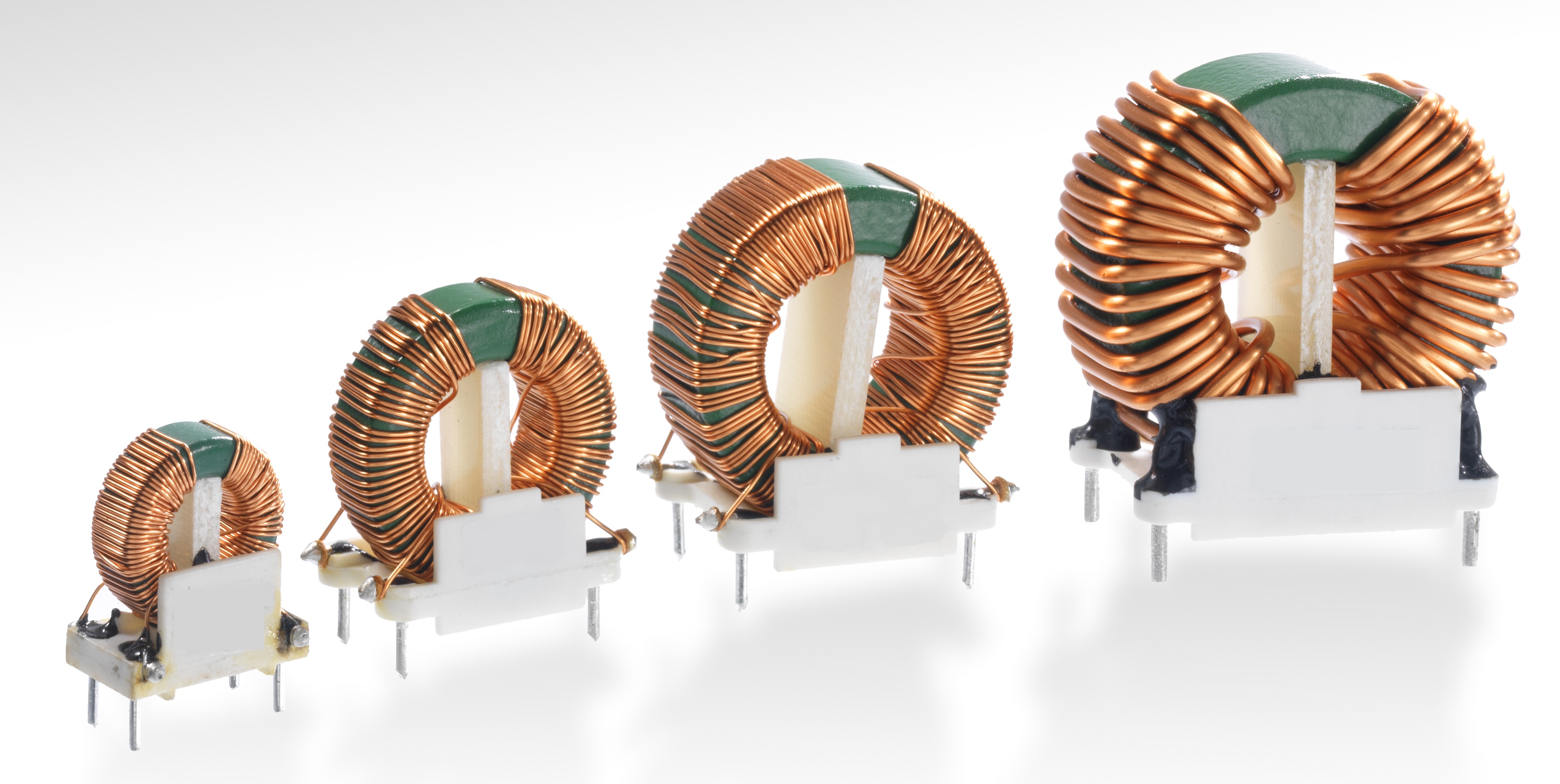
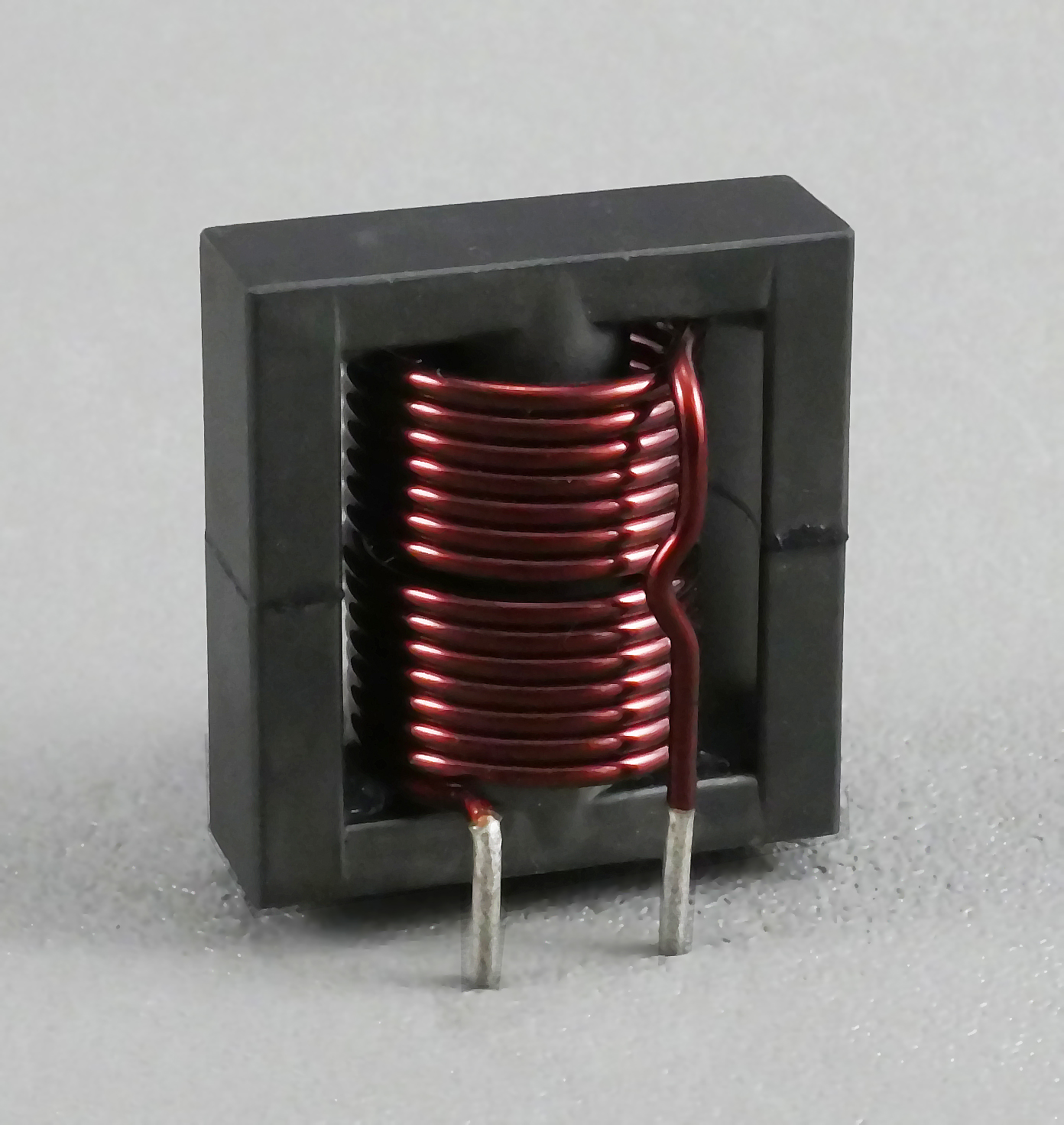
Power inductors are found in every application that requires current control — everything from small household appliances to electronic devices to the country’s power grid. For this reason, inductors are among the most important magnetic components in the industry.
Leakage Current Testing Requirements for Medical Grade Transformers
Across all types of industries and applications, transformers must meet specific performance and safety guidelines. But medical grade transformers, in particular, are subject to very stringent regulations in order to protect patient safety and well being.
10 Factors to Consider When Specifying a Custom Power Inductor
Power inductors can be used to filter the current or convert the Voltage and current to a different Voltage and current. Applications range from small electrical appliances to large power grid systems. Inductors consist of wound conductive metal coils that generate a magnetic field when electricity flows through them. Inductors are essential in any application that needs to carefully control [...]
What Is Litz Wire and Its Applications
Our engineering team frequently receives questions about whether we use Litz wire in our designs. We decided to focus this blog on educating our clients on this subject and explain why Litz wire is so ideal for certain applications and industries. Using Litz wire is associated with a number of benefits, including:
Food and Beverage Applications for Class 2/3 Power Transformers
Transformers convert alternating current (AC) from one voltage to a higher or lower voltage. Class 2 transformers are safer, more highly-rated electrical components frequently used in the food and beverage industry. Class 2 is a compliance rating signifying that the power transformer meets safety standards that reduce the risks of fire or shock.
Round Wire vs. Flat Wire
Power transformers play an important role in many electronics and electrical applications, each of which has distinct performance requirements. When designing a transformer, wire selection is one of the most important considerations. Round and flat wires each offer unique benefits and drawbacks for certain applications. Below, you can learn more about the characteristics of flat wire vs. round [...]
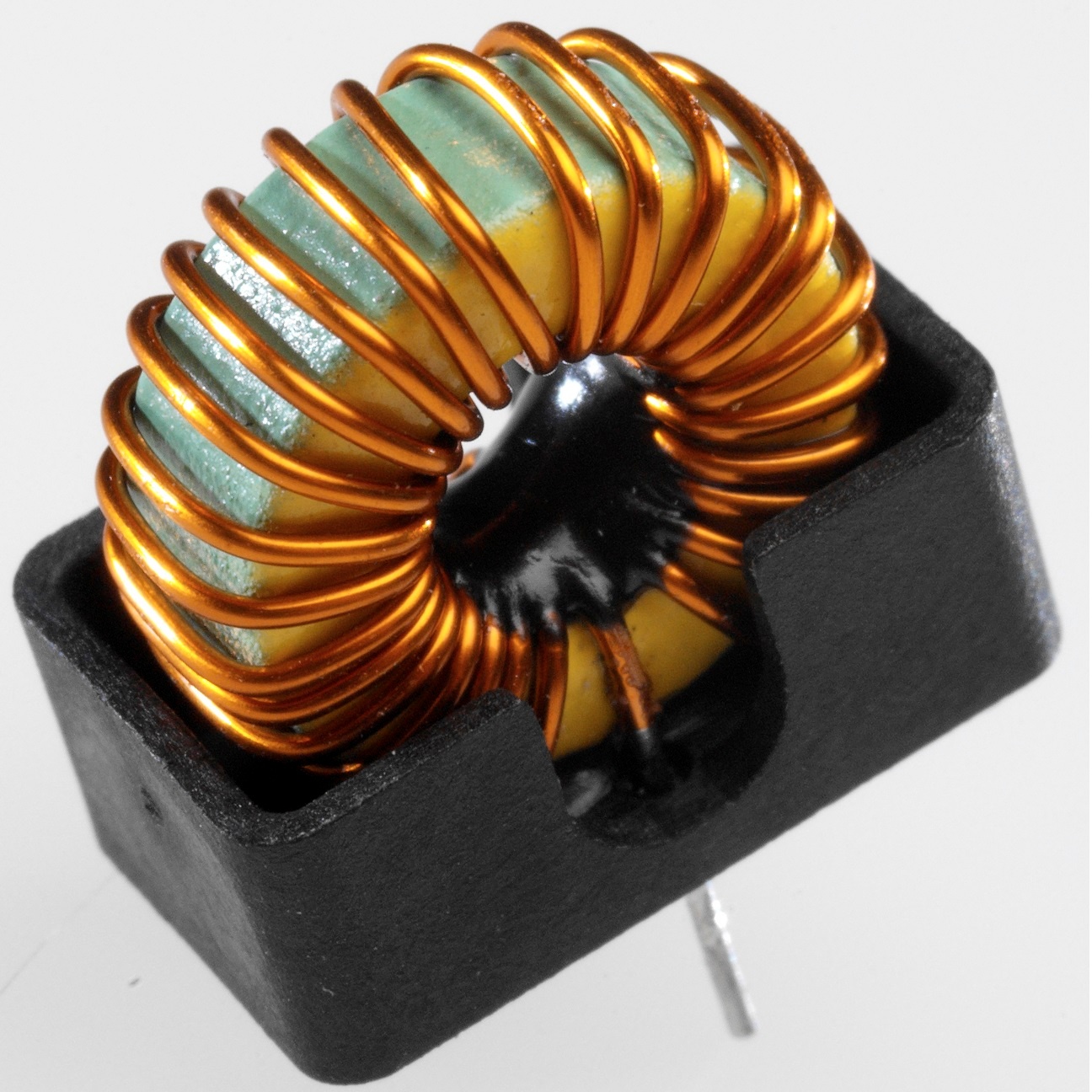
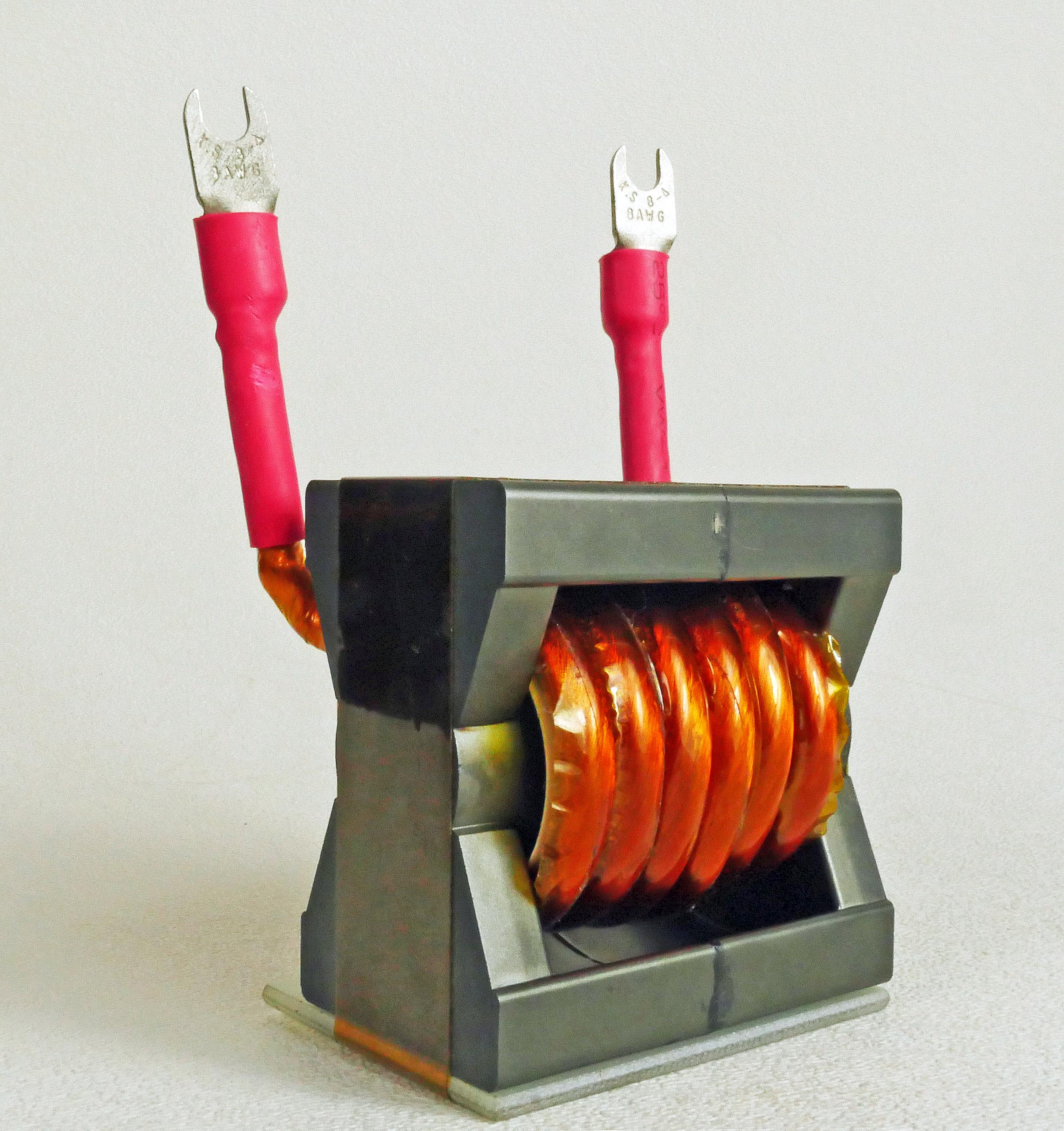
Chokes vs. Inductors
Numerous technologies rely on chokes or inductors to deliver, alter, and filter electrical current. Understanding the difference between chokes and inductors is essential when designing devices and machinery that rely on electrical power. These electrical components each suit specific applications.
Common Mode Chokes
A choke is a magnetic inductor used to block or limit unwanted high-frequency alternating current (AC) while allowing the desired lower frequency direct current (DC) to pass through. The choke acts as a filter for the noise produced by other radio signaling devices, inverters, and unshielded equipment, thereby reducing interference in electrical and electronic devices and systems.







.jpeg)




.jpg)
